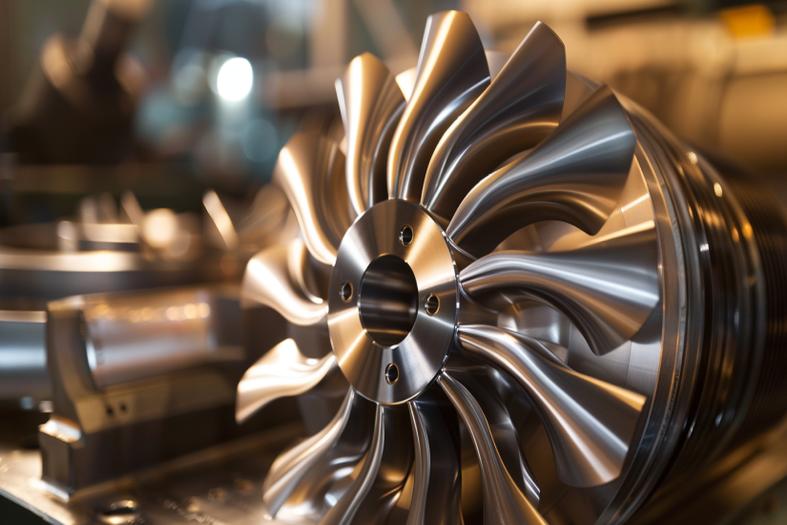
Have you ever struggled with inconsistent product quality, production delays, or wasted materials in your manufacturing process? These challenges can drain resources, damage your reputation, and hinder business growth. But there’s a solution that can transform your entire production approach: CNC machining.
As the founder of PROMACHINED, I’ve seen first-hand how CNC machining reshapes manufacturing with precision, speed, and efficiency. It’s not just about making parts — it’s about redefining what’s possible in modern manufacturing. Let me walk you through how this technology can solve common industry pain points while boosting your production capabilities.
CNC machining is an automated manufacturing process where computer-controlled machines create precise parts by following pre-programmed design instructions. It ensures high accuracy, efficiency, and repeatability in producing complex components.
CNC Machining Processes Include:
- Milling: Removing material using rotating cutters.
- Turning: Rotating the workpiece while cutting tools shape it.
- Drilling: Creating precise holes in the material.
- Grinding: Smoothing surfaces for a fine finish.
- EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): Shaping hard metals using electrical sparks.
- Laser Cutting: Cutting materials with a focused laser beam.
- Plasma Cutting: Cutting through electrically conductive materials using plasma torches.
- Water Jet Cutting: Using high-pressure water jets mixed with abrasives to cut materials.
Understanding CNC Machining: A Beginner’s Overview
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining automates the control of machine tools using computer software. It is widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing due to its precision and efficiency.
CNC machines interpret digital instructions from CAD (Computer-Aided Design) files, transforming virtual models into physical components while minimizing human error and ensuring repeatable results.
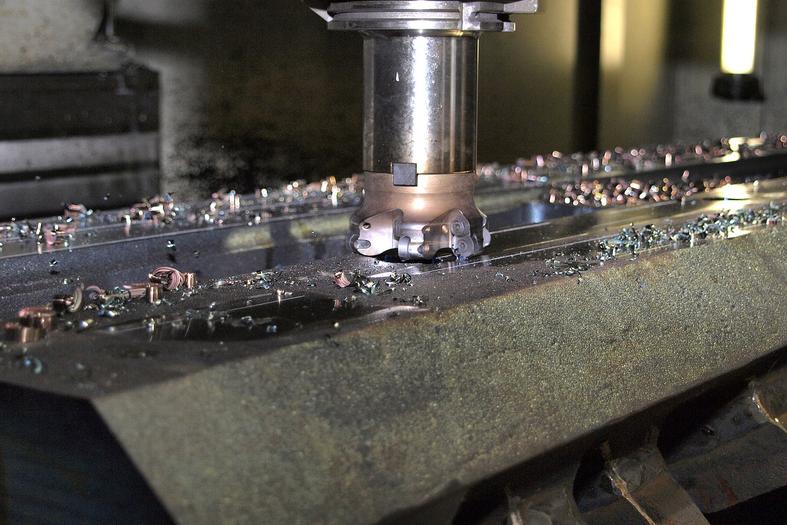

CNC Machining Workflow
- Design Creation (CAD Modeling): Engineers create a 3D model using CAD software, defining exact dimensions and specifications.
- Converting Design to Machine Code (CAM Processing): The design is translated into CNC-compatible code, generating tool paths and machining instructions.
- Machine Setup: The machine is prepared by securing the raw material and attaching the cutting tools. Operators also configure machine parameters like speed, feed rate, and cutting depth.
- Machining Execution: The CNC machine follows programmed instructions to cut, drill, or mill the material. Advanced sensors monitor the process to ensure precision and detect issues.
- Quality Inspection: Finished parts undergo strict inspections, including dimensional checks, surface assessments, and tolerance verification.

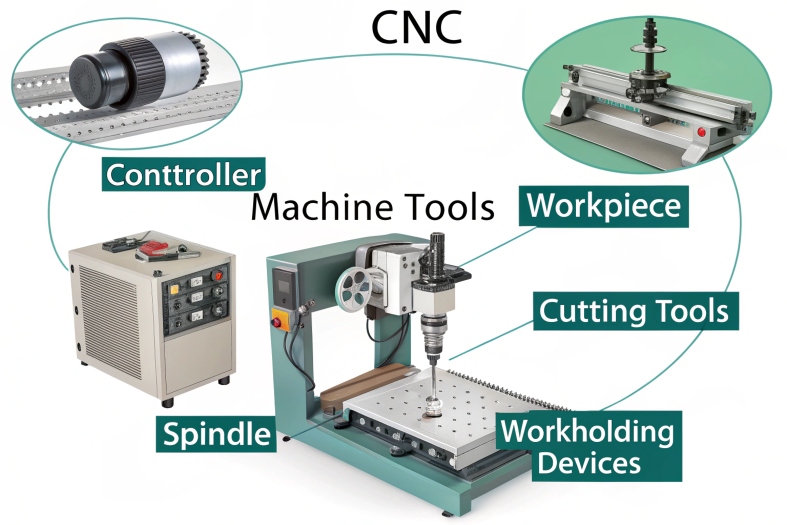
Key CNC Machine Components
- Controller: The brain of the CNC machine, interpreting code.
- Machine Tools: Devices like lathes, mills, and routers used to shape materials.
- Workpiece: The raw material being machined.
- Cutting Tools: Precision tools for cutting, drilling, and shaping.
- Spindle: A rotating component that holds the cutting tool.
- Workholding Devices: Fixtures, vises, and clamps securing the workpiece during machining.
Advantages of CNC Machining
- High Precision: Maintains strict tolerances.
- Repetitive Accuracy: Consistently produces identical parts.
- Efficiency: Automates production, reducing manual labor.
- Material Versatility: Works with metals, plastics, and composites.
- Scalability: Suitable for both prototyping and mass production.

Common Applications
- Automotive Parts: Engine components, gears, and custom parts.
- Medical Devices: Surgical instruments and prosthetics.
- Aerospace Components: Structural parts for aircraft.
- Electronics: Circuit boards, enclosures, and connectors.
- Consumer Products: Custom hardware, sporting goods, and home appliances.
Challenges in CNC Machining
- High Initial Costs: Machine setup and programming expenses are significant.
- Skilled Labor Requirement: Trained operators are needed.
- Material Waste: Incorrect settings can cause material loss.
- Maintenance Needs: Regular maintenance ensures optimal machine performance.
FAQ:
1. What Materials Can Be CNC Machined?
CNC machines can work with metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium, as well as plastics like ABS and nylon.
2. Is CNC Machining Expensive?
Initial setup costs are high, but large production runs become cost-effective.
3. How Accurate Is CNC Machining?
Precision can reach tolerances as tight as ±0.001 inches.
4. Can CNC Machines Handle Complex Designs?
Yes, CNC machining excels at producing intricate and detailed components.
5. Which Industries Rely on CNC Machining the Most?
Automotive, aerospace, medical, electronics, and consumer goods industries heavily depend on CNC machining.
Conclusion:
CNC machining plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing, combining high precision with efficiency. Understanding the process helps you appreciate how everyday products like car parts and medical devices are made.I personally invite you to reach out and discuss how we can support your next project. Contact us for a personalized quote.📧 Email: info@promachined.com


