A 4-axis CNC milling machine works by moving a cutting tool along X, Y, and Z axes while rotating the workpiece around the A-axis, allowing complex part geometries and multi-sided machining in a single setup.
Introduction to 4-Axis CNC Milling
In modern manufacturing, achieving precision and efficiency is essential. A 4-axis CNC milling machine stands out by offering an additional axis of movement beyond traditional 3-axis machines, enabling the creation of intricate components with reduced setups and machining time.
Key Components of a 4-Axis CNC Milling Machine
- Machine Bed: Supports the entire system, ensuring stability.
- Spindle: Holds and rotates the cutting tool.
- Rotary Table (A-Axis): Enables rotational movement, essential for 4-axis operation.
- Control Panel: Runs the machine through pre-programmed instructions (G-code).
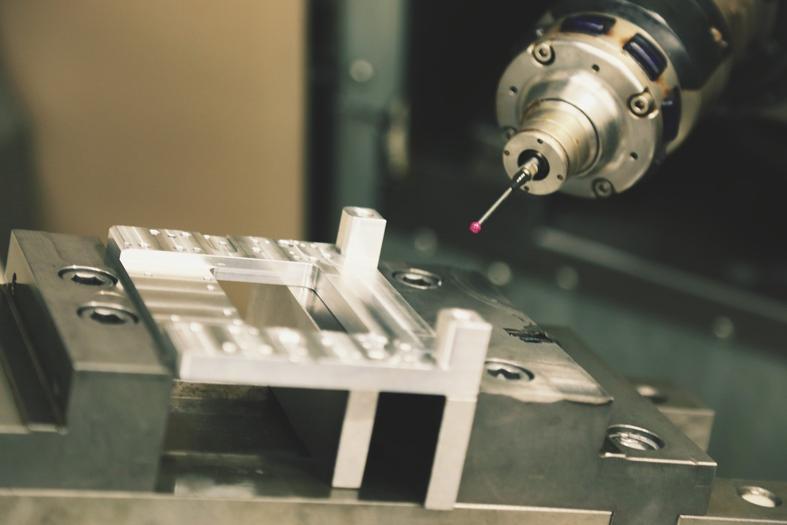
How It Works: Step-by-Step Process
- Design & Programming: CAD software designs the part, and CAM software generates G-code.
- Material Setup: The workpiece is clamped securely on the rotary table.
- Tool Selection: Automatic or manual tool changers load the appropriate cutting tools.
- Machining: The spindle rotates the tool while the rotary table turns the workpiece along the A-axis, allowing precise cuts from various angles.
Applications of 4-Axis CNC Milling
- Aerospace: Complex turbine blades and structural parts.
- Automotive: Engine components and suspension parts.
- Medical Devices: Surgical instruments and implants.
Advantages of 4-Axis CNC Milling
- Enhanced Precision: Reduces manual repositioning errors.
- Increased Efficiency: Machines multiple sides in one setup.
- Versatility: Handles complex shapes and materials.
Challenges and Limitations
- Higher Costs: More expensive than standard 3-axis machines.
- Programming Complexity: Requires skilled operators and advanced CAM software.
- Maintenance Demands: More components mean increased maintenance needs.

FAQ
1. What is the A-axis in a 4-axis CNC machine?
The A-axis allows rotational movement of the workpiece, enabling machining from different angles without manual repositioning.
2. How is 4-axis milling different from 3-axis milling?
4-axis milling includes a rotational axis, enabling more complex and precise machining compared to 3-axis milling.
3. What materials can be used in 4-axis CNC milling?
Common materials include metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium, as well as plastics and composites.
4. Is 4-axis CNC milling suitable for small businesses?
Yes, if the business requires high precision and complex parts, despite its higher initial investment.
Conclusion
Understanding how a 4-axis CNC milling machine works can be a game changer for businesses aiming for high-precision manufacturing. It combines multi-axis movement with precise control, reducing errors and boosting productivity. While there are upfront costs and technical learning curves, the long-term benefits in quality and efficiency make it a worthwhile investment for many industries. Whether you're crafting aerospace components or custom automotive parts, 4-axis CNC milling opens up a world of possibilities for advanced machining projects.


